The General Executive Bureau is comprised of the Secretariat and five bureaus, under which many divisions are set up to perform audits and administrative work.
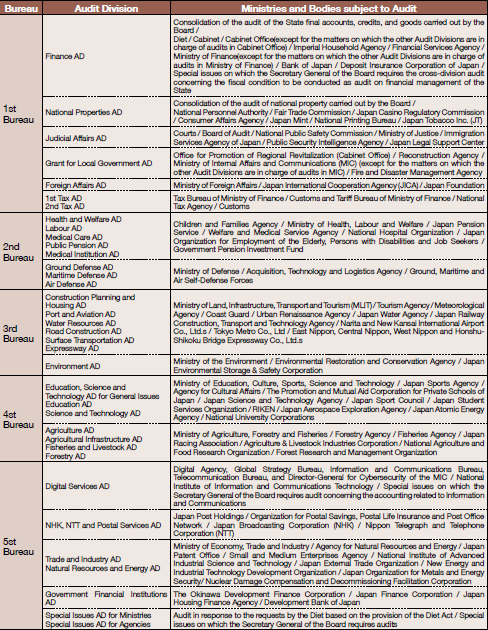
Audit activities are performed by the five bureaus. The following table shows the responsibility of each bureau and division.
Among these divisions, both the Special Issues Audit Division for Ministries and the Special Issues Audit Division for Agencies of 5th Bureau do not have any specific ministries or agencies subject to their mandatory audit, and conduct flexible and cross-cutting audits.
The number of authorized personnel of the General Executive Bureau is 1,251 (as of January 2025).
Many of these personnel are assigned to various audit divisions as auditors and assistant auditors.
The audit staff of the Board must have a high level of competency in auditing.
The term “Accounting,” that is subject to audit by the Board, does not just mean accounting for the incoming and outgoing funds or bookkeeping in a narrow sense, but covers broader issues of whether tax payersʼ money has been properly and effectively collected and used for implementing administrative activities of the State. Auditors of the Board therefore must have broad knowledge of not only management and operations of the auditees, but also of other relevant fields such as law, finance, economics, electricity, digital services, machinery, civil engineering, construction.
The Board recruits its staff from those who have passed the Public Service Entrance Examination conducted by the National Personnel Authority. Besides those who have specialized in law and economics, the Board recruits a considerable number of personnel who specialized in electricity, digital services, civil engineering, construction from a list of successful examinees.
The Board also utilizes outside expertise by recruiting mid-career staff or by employing as fixed-term staff from those who have specialized knowledge and skills, such as certified public accountants (CPA).
After recruitment, new staff members undergo extensive training and examinations in various fields to acquire necessary knowledge and skills, and then become auditors after several years of audit experience.
Auditors also have to attend advanced professional training in order to cope with more diversified and specialized administrative activities of the auditees.
To strengthen its training activities in order to improve the auditing competency of its staff, the Board established a training center and provides systematic training to its staff.